
How to Choose the Right Essential Oil for Your Life’s Season
Introduction Our lives move in seasons — moments of growth, rest, change, and renewal. Just as nature shifts with the rhythm of spring, summer, autumn,

Herbalism, the practice of using plant-derived substances for medicinal purposes, offers a diverse range of preparation techniques. These methods extract the therapeutic properties of plants, making them accessible for various health applications. Below, we explore the most effective ways to create herbal medicine.
Infusions are ideal for delicate plant parts like leaves and flowers. They are commonly used for herbal teas, providing gentle, water-soluble compounds. To make an infusion:
Best for: Chamomile, peppermint, and hibiscus.
Decoctions work well for roots, bark, and seeds, extracting a more concentrated liquid. To prepare a decoction:
Best for: Ginger, echinacea root, and cinnamon bark.
Tinctures are concentrated herbal extracts made using alcohol or a water-alcohol mixture. To create a tincture:
Best for: Valerian root, echinacea, and elderberry.
Maceration involves soaking plant material in cold water to extract mucilaginous substances. To prepare:
Best for: Marshmallow root, sage, and thyme.
Essential oils are aromatic compounds extracted through distillation or cold pressing. These oils are used for aromatherapy, topical applications, and natural remedies.
Best for: Lavender, tea tree, and eucalyptus.
Poultices involve applying crushed plant material directly to the skin. To prepare:
Best for: Arnica, comfrey, and plantain leaves.
Salves and balms are semi-solid, infused preparations for external use. To create a salve:
Best for: Calendula, arnica, and St. John’s wort.
Powdered plant material can be encapsulated or compressed into tablets for easy consumption. To prepare:
Best for: Turmeric, spirulina, and ashwagandha.
Herbal syrups blend plant extracts with sugar or honey to create a palatable remedy. To make a syrup:
Best for: Elderberry, ginger, and licorice root.
Herbal medicine offers a wide variety of preparation methods, each with unique benefits. Whether you’re making a simple infusion, a potent tincture, or a soothing salve, these natural remedies harness the power of plants to support health and well-being.

Introduction Our lives move in seasons — moments of growth, rest, change, and renewal. Just as nature shifts with the rhythm of spring, summer, autumn,

Imagine walking into a space that instantly soothes your spirit, calms your mind, and feels like a gentle embrace from nature itself. That’s the power
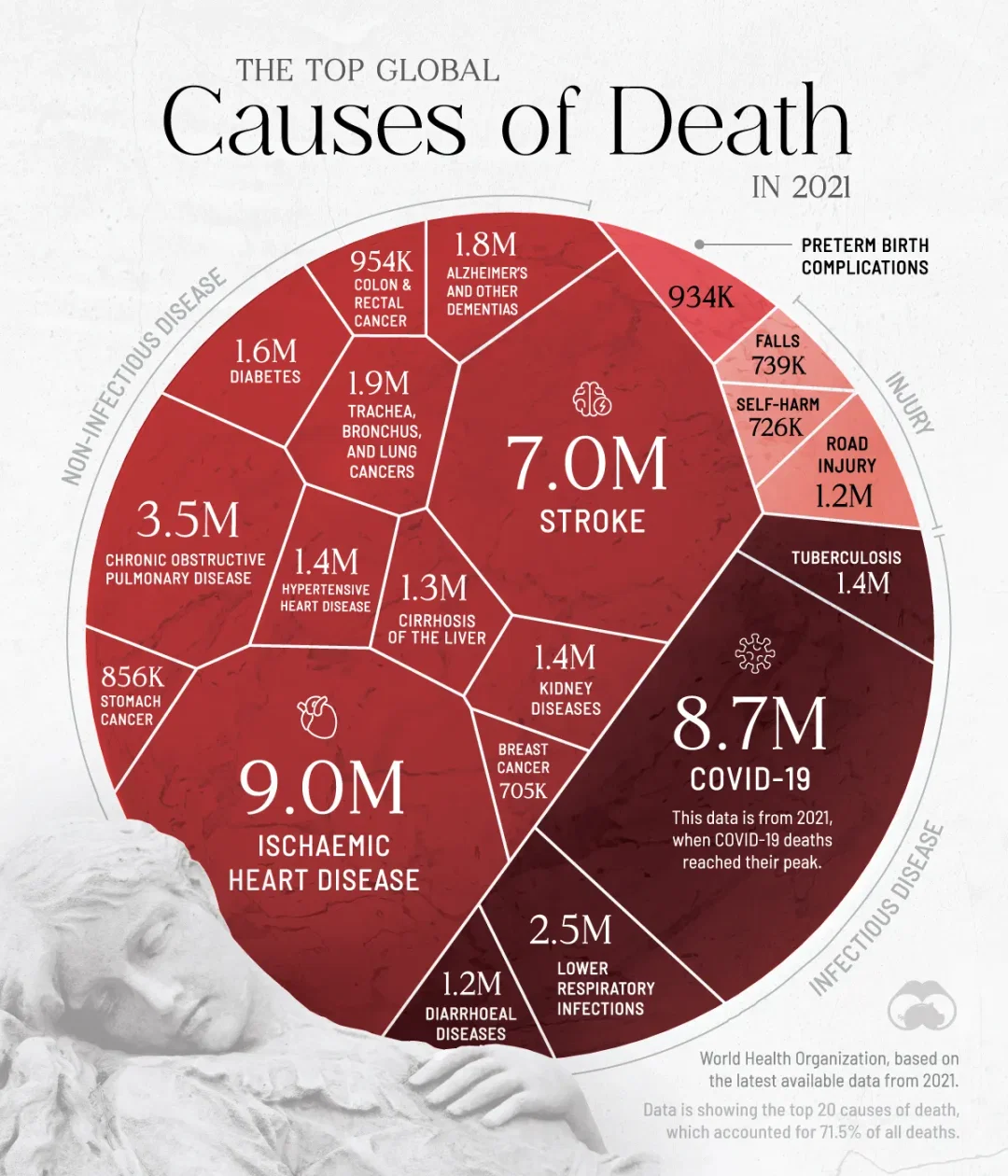
Every year, millions of people around the world lose their lives to just a handful of diseases. In fact, about 70% of all deaths are

What is the 08/08 Portal? Every year on August 8th, the powerful Lion’s Gate Portal opens — a cosmic alignment between Earth, the Sun, and

Have you ever felt disconnected from your higher self, experienced mental congestion, or found it hard to trust in your path? These may be signs

Do you sometimes feel disconnected from your intuition or experience mental fog? These may be signals that your Third Eye Chakra—also known as Ajna—is out